
The arrival of the steamship benefitted some countries but not others, with the strength and inclusiveness of institutions playing a key role
How does globalisation affect development? This question has a long tradition in economics and has been much debated both in the academia and in policy circles (e.g. Goldberg and Pavcnik 2017). Neoclassical theories tell us that reducing trade barriers across countries should provide net benefits to individual economies by making markets more efficient and stimulating competition. Testing these theories, however, turns out to be difficult as rich countries are generally also those that trade the most. Is it trade that makes countries rich, or do they trade more because they are rich to start with?
Trade and development
The ideal way to answer to these questions would be through an experiment, in which we randomly divide all the countries of the world into two groups and then we reduce trade costs for one group, while keeping trade costs constant for the other group. The difference in the observed GDP growth in the following years between the two sets of countries would eventually provide us with an estimate of the impact of trade integration on development.
It turns out that history can provide us with such an experiment! The invention of the steamship in the late 19th century greatly reduced trade costs for some countries but not for others. Whether a country was able to reduce its trade costs as a result of this innovation was the result of its geography, rather than economic forces. In a recent paper (Pascali 2017), I use this natural experiment to assess the causal impact of trade on development.
Trade routes and wind patterns
Before the steamship, sea routes were shaped by winds. As an example, consider Figure 1, which illustrates a series of journeys made by British sailing ships in the 19th century, between England, the Cape of Good Hope and Java, and Figure 2, which depicts the prevailing sea-surface winds in the world.
Figure 1 Fifteen journeys made by British ships between 1800 and 1860
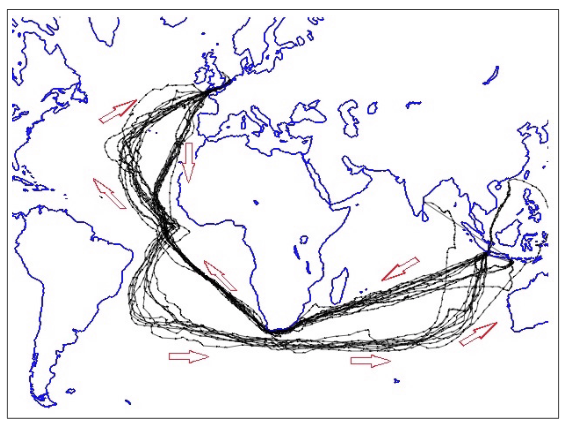
Notes: These journeys were randomly selected from the CLIWOC dataset among all voyages between England and Java comprised in the dataset.
Figure 2 Prevailing winds in May, 2000 to 2002
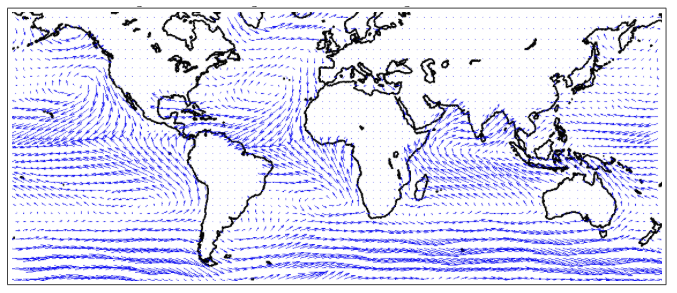
Note: direction of wind defined by the direction of the arrow and speed by the length of the arrow.
Winds tend to follow a clockwise pattern in the North Atlantic; consequently, sailing ships would sail westward from Western Europe after traveling south to 30 N latitude and reaching the ‘trade winds’, thus arriving in the Caribbean rather than traveling straight to North America. The result is that trade systems historically tended to follow a triangular pattern between Europe, Africa, the West Indies and the United States.
South Atlantic winds tend to blow counter-clockwise. Consequently, sailing ships would not sail directly southward to the Cape of Good Hope; rather, they would first sail southwest toward Brazil and then move east to the Cape of Good Hope at 30 S latitude.
The steamship and globalisation
The invention and subsequent development of the steamship was a watershed event in maritime transport and was the major driver of the first wave of trade globalisation (1870-1913), an increase in international trade that was unprecedented in human history. For the first time, vessels were not at the mercy of the winds, and trade routes became independent of wind patterns.
The steamship, however, reduced shipping times in a disproportionate manner across trade routes, depending on the type of winds that vessels used to face throughout their journeys. In some routes, shipping times were cut by more than half, while in some others the change was minimal. These asymmetric changes in shipping times (and related trade costs) across countries are used to explore the effect of international trade on economic development.
Findings: Economic divergence and constraints on executive power
Exploiting the random variation in trade costs, generated by the transition from sail to steam, I document that the consequences of the first wave of trade globalisation on development were not necessarily positive. On a sample of 36 countries, the average short-run impact was reductions in per-capita GDP, population density and urbanisation rates. This average negative impact, however, masks large differences across different groups of countries.
First, the initial wave of trade globalisation turned out to be particularly detrimental in countries that were already less economically developed to start with and it was probably the major reason behind the Great Divergence (the economic divergence observed between the richest countries and the rest of the world in the second-half of the 19th century).
Second, trade turned out to be very beneficial to countries that were characterised by strong constraints on executive power, a distinct feature of the institutional environment that has been demonstrated to favour private investment.
The crucial role of institutions
Why should we expect institutions to be crucial to benefitting from trade? A common argument is that a country with ‘good’ institutions will suffer less from the hold-up under-investment problem in those industries that intensively rely on relationship-specific assets. The hold-up problem is where two parties refrain from cooperating because of concerns that they may give the other party increased bargaining power, and thereby reduce their own profits. In this sense, good institutions are a crucial source of comparative advantage in non-agricultural sectors, in which the hold-up problem is more binding.
My results confirm this theoretical prediction – a reduction in trade costs increased the share of exports in non-agricultural products, and consequently the share of the population living in large cities, only in those countries characterised by stronger constraints on executive power.
Conclusions
How did the rise in international trade affect economic development? I found that:
- the adoption of the steamship had a major impact on patterns of international trade worldwide;
- only a small number of countries, characterised by more inclusive institutions, benefited from trade integration; and
- globalisation was the major driver of the Great Divergence.
Policymakers who are willing to learn from history are advised to consider that a reduction in trade barriers across countries does not automatically produce (at least in the short run) large positive effects on economic development and can increase inequality across nations.
References
Goldberg, P and N Pavcnik (2017), "Trading up: Globalisation and developing countries", VoxDev, 21 June.
Pascali, L (2017), “The Wind of Change: Maritime Technology, Trade, and Economic Development”, American Economic Review 107(9).

